MVC (Model-View-Controller) is one of the most well-known and least-understood decomposition patterns.
The MVC approach was introduced in “fat” client applications. Model, View, and Controller in such applications were all loaded in memory and could interact immediately:
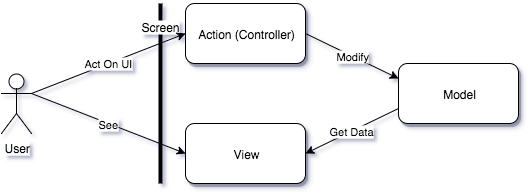
- User clicks on a button in UI, which triggers Controller action
- Controller action calls business logic on Model, Model changes its state
- Since View observes Model, it is automatically re-rendered
- User sees the new UI
The design had the following benefits:
- The presentation Layer (View and Controller) is separate from the business logic (Model)
- Model knows nothing about its presentation
- Controller knows nothing about View. It only interprets user input and passes it to the Model.
- It follows the CQRS (Command Query Responsibility Segregation) principle: state-modifying infrastructure (Controller) is different from state-receiving infrastructure (View). Their complexity is separated.
Later web applications adopted the MVC approach. But some of the web frameworks implemented it differently:
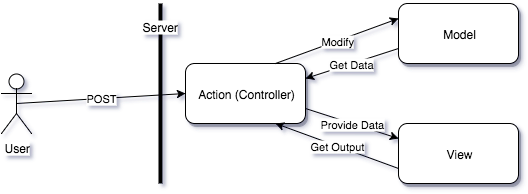
There are a couple of problems with such implementation:
- state modification and state representation both happen in one web request. It is a violation of the HTTP protocol.
- Controller does all the communication. It knows about both models and views. It violates CQRS and combines the complexity of both the View and Controller.
By design, HTTP protocol follows the CQRS principle: commands (POST, PUT, DELETE) must be separate from queries (GET). So if we follow HTTP, we will follow CQRS on the communication layer:
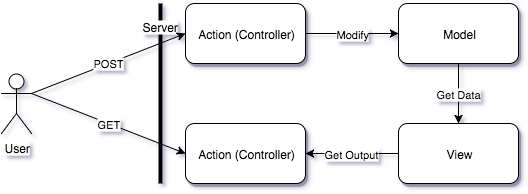
Here data retrieval request (GET) is separated from data modification (POST), but Controller is still an entry point for both violating the CQRS principle on the application level. A lot of modern web frameworks are built this way.
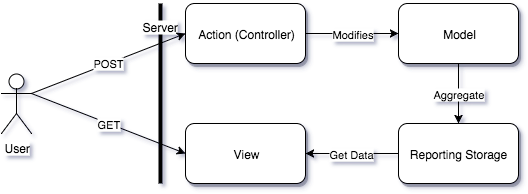
One simple step is needed to build a proper client-server MVC: remove the Controller from the data retrieval request.
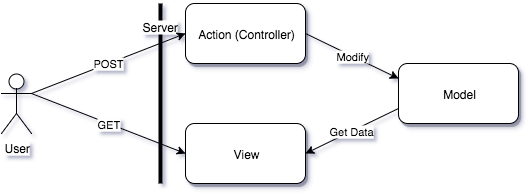
You can see that this diagram is almost identical to the initial correct fat-client MVC diagram:
- Controller only does state modification.
- View only does state representation.
- Both respond to the request directly.
Both MVC and HTTP follow the CQRS principle.
If we apply CQRS further, we will separate our business operations infrastructure from reporting:
One of the evolution branches of the CQRS principle is Event Sourcing architecture.